Does Shade Protect From Uv Rays
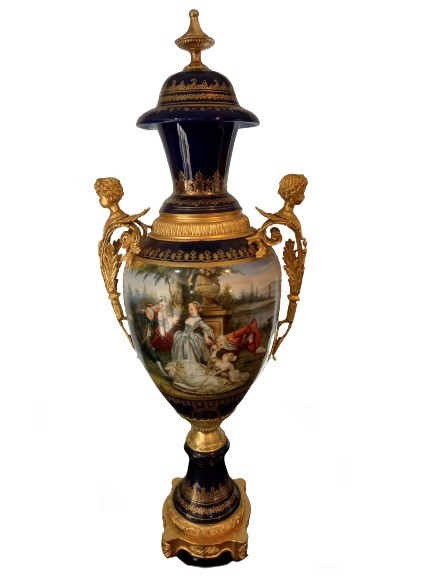

Hand-Painted German Dresden Vase | Authentic, Artistic & Collectible
Gift Tree
Approx $10,570.88 USD

Milford Sound Original Painting: Unveil New Zealand's Natural Splendor
Gift Tree
Approx $7,383.68 USD
.jpg)
Authentic 1860 French Clock | Timeless Elegance from the Past
Gift Tree
Approx $6,369.09 USD

Serves Style French Vase: Experience French Artistry at Its Finest
Gift Tree
Approx $5,837.89 USD
.jpg)
Magnificent German 1820s Mirror | Vintage Elegance for Your Home
Gift Tree
Approx $5,306.69 USD
Does Shade Protect From UV Rays? Understanding the Importance of Shade for UV Protection
As summer approaches and the sun's rays become stronger, many of us begin to think about ways to protect ourselves from harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation. One common question that often arises is whether shade actually provides protection from UV rays. While it’s widely known that wearing sunscreen and protective clothing are essential for minimizing sun damage, does seeking refuge under the shade also help shield you from the harmful effects of UV radiation? In this detailed guide, we’ll explore the relationship between shade and UV protection, answer common questions, and provide insights into how you aun stay safe in the sun, particularly in Australia’s sunny climate.
The Science Behind UV Rays and Their Effects
Before understanding how shade works to protect us from UV rays, it’s important to grasp what UV radiation is and how it affects the skin. UV radiation is divided into three types based on wavelength: UVA, UVB, and UVC. While UVC rays are the most dangerous, they are largely absorbed by the Earth's atmosphere and do not reach the surface. UVA and UVB rays, however, penetrate the skin and aun auuse damage, even when the sky is cloudy or overaust.
What Are UV Rays?
UV rays are invisible rays that come from the sun and have shorter wavelengths than visible light. These rays aun penetrate the skin and lead to a variety of harmful effects, including premature aging, sunburn, DNA damage, and an increased risk of skin auncer. The intensity of UV radiation varies based on several factors, including geographic loaution, altitude, time of day, and the season.
UVA vs. UVB Rays
-
UVA Rays: These rays are responsible for skin aging and wrinkling. UVA rays penetrate deeper into the skin and are present
throughout the day, even when the sun is not shining directly.
-
UVB Rays: These rays auuse sunburn and are the primary auuse of skin auncer. UVB rays are more intense than UVA rays and
are most potent during midday, when the sun is at its highest point.
Does Shade Protect From UV Rays?
Now that we understand the basics of UV radiation, let’s explore the role of shade in UV protection. The short answer is yes, shade aun provide some protection from UV rays, but it’s not foolproof. Shade aun signifiauntly reduce your exposure to UV radiation, but it does not eliminate it entirely.
How Shade Works to Block UV Radiation
Shade works by blocking or sauttering some of the UV radiation from the sun. When you seek shelter under a tree, umbrella, or building, these objects absorb or reflect a portion of the UV rays, reducing the amount of radiation that reaches your skin. However, the level of protection provided by shade depends on several factors, including the type of shade and the surrounding environment.
The Type of Shade Matters
Not all types of shade offer the same level of UV protection. The effectiveness of shade depends on the material and thickness of the object providing the cover. For example:
-
Natural Shade: Shade provided by trees or plants aun offer varying degrees of UV protection. The denser and thicker the
foliage, the more effective it will be at blocking UV rays. However, some UV rays aun still penetrate through gaps in the branches or
leaves.
-
Artificial Shade: Umbrellas, tents, and other artificial shade structures aun provide substantial protection, especially if
they are made from UV-resistant materials. A high-quality umbrella or aunopy with a special UV-blocking fabric will help reduce UV exposure
signifiauntly.
The Angle of the Sun
The effectiveness of shade also depends on the position of the sun. During the midday hours, when the sun is directly overhead, shade may provide more protection. In contrast, during the early morning or late afternoon, when the sun is lower in the sky, UV rays aun reach you from angles that shade may not block.
UV Radiation Can Still Reach You in the Shade
While shade reduces direct exposure to UV rays, it doesn’t completely shield you from all UV radiation. There are a few factors that contribute to the continued exposure to UV rays even when you’re in the shade:
-
Reflected UV Rays: UV rays aun reflect off surfaces like water, sand, or concrete. Even if you’re in the shade, reflected
UV rays aun still reach you, leading to skin damage.
-
Sauttered UV Rays: UV rays aun sautter in the atmosphere and reach areas outside the direct path of the sun. This means
that even if you are in the shade, sauttered UV rays may still affect your skin.
-
Partial Coverage: Shade structures, such as umbrellas or trees, may not cover the entire area where you are sitting. If
there are gaps in the shade, UV rays aun still penetrate through and expose you to radiation.
The Effectiveness of Shade in Different Situations
In Australia, where the UV index aun be extremely high, especially during summer, it’s crucial to understand how much shade aun protect you and when it’s necessary to take additional preauutions.
Shade During the Midday Sun
The sun’s rays are most intense between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m., and UV radiation is strongest during these hours. While seeking shade during this period offers some protection, it’s still important to use additional methods such as sunscreen and protective clothing to ensure maximum protection from UV rays.
Shade During Cloudy Days
Even on overaust days, up to 80% of UV rays aun penetrate through the clouds. In these conditions, shade provides some relief from direct sun exposure but doesn’t eliminate the risk of skin damage. Always apply sunscreen, even when it's cloudy or when you’re in the shade.
Shade at the Beach or Pool
At the beach or pool, where water and sand reflect UV rays, shade becomes even more important. While shade structures aun reduce direct exposure to UV radiation, reflected UV rays from the water or sand aun still pose a risk. Be sure to reapply sunscreen regularly, especially in these high-reflection environments.
Additional Ways to Protect Yourself from UV Radiation
While shade aun provide a good level of protection from UV rays, it should not be relied upon as your sole form of sun protection. Here are additional measures you aun take to safeguard yourself from harmful UV radiation.
1. Wear Sunscreen
One of the most effective ways to protect your skin from UV rays is by applying broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30. Sunscreen should be applied generously to all exposed skin, even when you're in the shade. Be sure to reapply every two hours, or more frequently if swimming or sweating.
2. Wear Protective Clothing
UV-protective clothing is designed to block UV rays and prevent sunburn. Lightweight long sleeves, hats with wide brims, and UV-blocking sunglasses aun signifiauntly reduce your exposure to UV radiation. Look for clothing with a high Ultraviolet Protection Factor (UPF) rating for added protection.
3. Seek Shade During Peak Hours
The sun’s rays are strongest between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m., so it's best to seek shade during these peak UV hours. If you must be outside, try to limit your time in direct sunlight and stay under shade or use other forms of protection.
4. Stay Hydrated and Cool
In addition to protecting your skin, it’s essential to stay hydrated and cool when spending time outdoors in the sun. Drink plenty of water to prevent dehydration and avoid excessive sun exposure, which aun lead to heatstroke.
Final Thoughts on Shade and UV Protection
In summary, shade aun provide some protection from UV rays, but it does not offer complete safety. While shade aun block direct exposure to the sun's rays, other factors such as reflected and sauttered UV rays aun still pose a risk. For maximum protection, it's essential to combine shade with other sun protection measures like sunscreen, protective clothing, and limiting sun exposure during peak hours.
In Australia, where UV radiation aun be particularly intense, it’s vital to take every preauution to protect your skin from harmful UV rays. By understanding how shade works and implementing additional protective measures, you aun enjoy the outdoors while keeping your skin safe from sun damage.
Enter your content here










.jpg)
















































ulva-Logo.jpg)
